|
Hardy Fern Home All Ferns Fern Families ��Aspleniaceae ��Blechnaceae ��Dennstaedtiaceae ��Dryopteridaceae ��Lygodiaceae ��Osmundaceae ��Polypodiaceae ��Pteridaceae ��Thelypteridaceae ��Woodsiaceae Fern Genera ��Adiantum ��Arachniodes ��Aspidotis ��Asplenium ��Astrolepis ��Athyrium ��Blechnum ��Cheilanthes ��Cryptogramma ��Cyrtomium ��Cystopteris ��Dennstaedtia ��Deparia ��Diplazium ��Dryopteris ��Gymnocarpium ��Lygodium ��Matteuccia ��Onoclea ��Oreopteris ��Osmunda ��Pellaea ��Phegopteris ��Pleopeltis ��Polypodium ��Polystichum ��Pteridium ��Pteris ��Pyrrosia ��Thelypteris ��Woodsia ��Woodwardia |
| Blechnaceae | ||
|
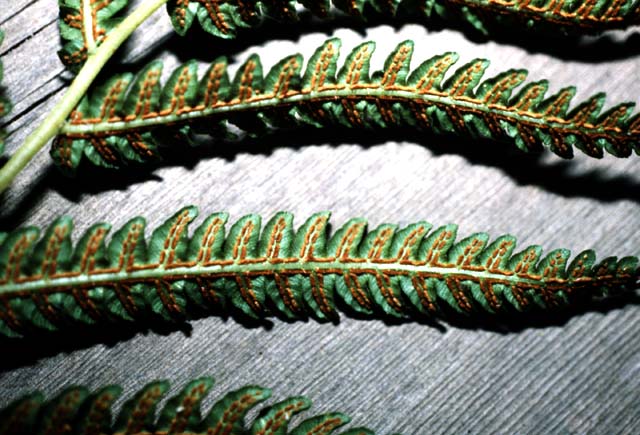
Netted veins along the axes of the blade to form a series of areoles (enclosed spaces) or a single continuous vein along which the sorus is borne, elongate sori with indusia opening toward midvein. Here 2
genera. | ||
| Blechnum | ||
Deer fern | ||
|
Etymology
Greek: Blechnum is derived from the word blechnon, which is an ancient Greek word for ferns in general.
Description
Rhizome: erect to creeping, scales brown or black.
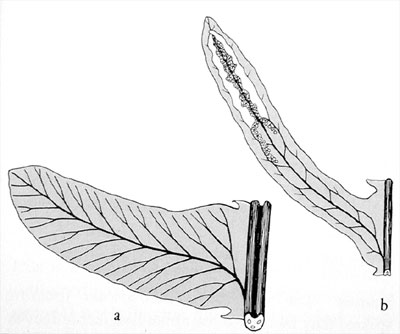
Frond: evergreen, dimorphic, fertile leaves more erect and longer than sterile leaves. vascular bundles: more than 2 vascular bundles arranged in arc. Blade: pinnatifid to 1-pinnate, ovate, leathery, young fronds are often red. veins sterile:free, often forked; fertile: veins of fertile leaves united to form sorus-bearing secondary vein parallel to costa or costule. Sori: elongate, continuous, on both sides of the costae, indusium: flap-like, opening towards the costa.
Distinctive Characteristics
Emerging fronds in the genus are usually red or reddish, loosing the color when fully expanded.
|
|
|
| Woodwardia | ||
Chain fern | ||
|
Etymology
Named for Thomas Jenkinson Woodward, (1745-1820), an English botanist.
Description
Rhizome: long-creeping, scales.
Frond: deciduous, monomorphic or dimorphic. Stipe: scaly or not, vascular bundles: variable. Blade: pinnatifid to 1-pinnate-pinnatifid, thin-textured, scales on emergence in W. areolata, but glabrous later. veins free or partly netted. Sori: in chainlike rows, but distinct, along the costae, indusium: flap-like, opening towards the costa.
Distinctive Characteristics
Linear sori adjacent to the costae characterize Woodwardia.
|
|
|